Reverse Skin Aging: Top Advanced Techniques for Tightening & Firming
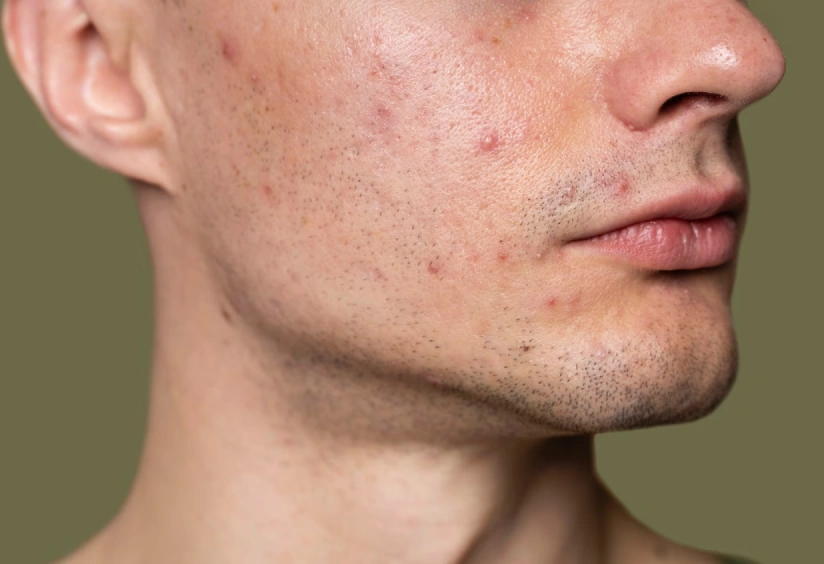
Fungal acne, often confused with regular acne breakouts, has to be properly understood and identified to ensure appropriate treatment. It’s a distinct skin condition, triggered by an overgrowth of a yeast/fungus on the skin of most people. Traditional acne treatments usually don’t work for this type of acne.
In this blog, we’ll build your thorough understanding of fungal acne by discussing its symptoms, causes, prevention, and the best fungal acne treatment options in Delhi.
Fungal acne, medically referred to as Malassezia folliculitis, is a skin condition in which hair follicles become infected with Malassezia, a yeast-like fungus. Though Malassezia normally grows on the skin, its overgrowth causes itchy, uniform, tiny bumps on the skin- the fungal acne. This condition worsens with sweat build-up, humidity, and the wrong choice or use of skincare products.
| Features | Fungal Acne (Malassezia Folliculitis) | Bacterial Acne (Acne Vulgaris) |
| Cause | It’s the result of plugging of hair follicles with overgrown yeast/fungus called Malassezia. | It’s the result of clogging of pores with extra sebum, dead skin cells, dirt, and a bacterium named Cutibacterium acnes. |
| Characteristics / Appearance | The plugged hair follicles show up as tiny, uniform, red or skin-colored bumps or as whiteheads. | There are varied lesions: black or white comedones, red papules, pustules (pimples), cysts, and nodules. |
| Sensation | The bumps are often very itchy, especially when the skin is hot or sweaty. | The lesions can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory. Often, they feel sore and tender, sometimes painful. |
| Areas commonly affected | The condition often develops on the upper arms, chest, back, shoulders, and hairline/forehead. | Most often, the lesions develop in oily or hormone-affected areas like the jawline and cheeks, neck, back, and shoulders. |
| Effective Treatments | Antifungal medications can only be the solution. | Typical products for acne, like topicals containing benzoyl peroxide, reti-noid, and salicylic acid; antibiotics, comedone extraction, or hormonal therapy, are recommended. |
Suspect fungal acne if experiencing the following symptoms:
Fungal acne results from the rapid multiplication of Malassezia yeast, which normally resides on the skin at low levels. When hair follicles become plugged with excess oil, sweat, and dead skin cells, or when the skin's natural balance is disturbed, Malassezia overgrows. The overgrowth leads to infection and subsequent inflammation of the hair follicles- the fungal acne breakout.
The main causative factors or triggers of fungal acne include:
Fungal acne mostly affects:
Only a certified dermatologist accurately identifies fungal acne through:
Fungal acne can be best addressed with prescription oral antifungals, antifungal washes, and antifungal creams/lotions/ointments, along with lifestyle modifications.
Usually, dermatologists prescribe ketoconazole-based products, and when fungal infections are severe or widespread, they recommend pills like fluc-onazole or itrac-onazole. They also recommend zinc pyrith-ione, salicylic acid, or selenium sulfide-containing washes.
The main indicators to consult a skin doctor for fungal acne include:
Fungal acne is not a variant of regular acne, but rather a skin condition where hair follicles get infected by Malassezia, a yeast overgrowth. A medical consultation with a certified dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Timely creation and execution of the right treatment plan, in combination with the right skincare and healthy lifestyle, will only help make the skin clear and healthy and prevent further flare-ups of fungal acne.
If you suspect fungal acne and need professional treatment, see a leading dermatologist in Delhi at Delhi Wellness Clinic. The dermatologist at the clinic provides treatment for all types of acne and helps people achieve smoother, healthier skin. Contact for details.